This is an indefinite integral,
so we need to find
the most general
antiderivative of the integrand f(n).
To find an antiderivative of
f(
n), we go through
our list of integration methods:
- Recognize elementary antiderivatives
- Rewrite the integrand to make it easier
- Use substitution to reverse the chain rule or simplify the
integrand
- Use integration by parts
- Use inspection to see the value of a definite
integral
to find one that works for this integrand. In this case,
only one method is appropriate. We can rewrite the integrand: use properties of logarithms to rewrite the log term to give an expression that is more easily integrable.
This is shown below.
Rewriting:
Use properties of logarithms to rewrite the log term to rewrite the integral:
( ln(n3) )/n
=
3 ln(n)/n.
Thus,
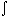
( ln(
n3) )/
n dn
=
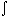
3 ln(
n)/
ndn
which can be evaluated using
substitution, to obtain
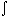
3 ln(
n)/
ndn
=
((3/2) ln(
n)
2) +
C.
Explanation for rewritten term(s)
SubstitutionLet
w = ln(
n). Then
w' = 1/
n, so
dw = (1/
n)
dn.
The integral can therefore be rewritten as
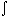
3 ln(
n)/
n dn =
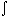
3
w dw =
(3/2)
w2 +
C
Thus, substituting back for
w,
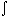
3 ln(
n)/
n dn =
(3/2) ln(
n)
2 +
C